结构设计
class MyQueue {
Stack<Integer> data;
Stack<Integer> help;
public MyQueue() {
data = new Stack<>();
help = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
help.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
if (data.isEmpty() && help.isEmpty()) throw new RuntimeException("empty queue");
if (data.isEmpty()) {
while (!help.isEmpty()) data.push(help.pop());
}
return data.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if (data.isEmpty() && help.isEmpty()) throw new RuntimeException("empty queue");
if (data.isEmpty()) {
while (!help.isEmpty()) data.push(help.pop());
}
return data.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return data.isEmpty() && help.isEmpty();
}
}方法1:Stack
方法2:Deque
方法1:两个队列
方法2:一个队列
方法1:辅助栈[浪费空间]

方法2:辅助栈[不浪费空间]
方法1:二分
方法2:线段树
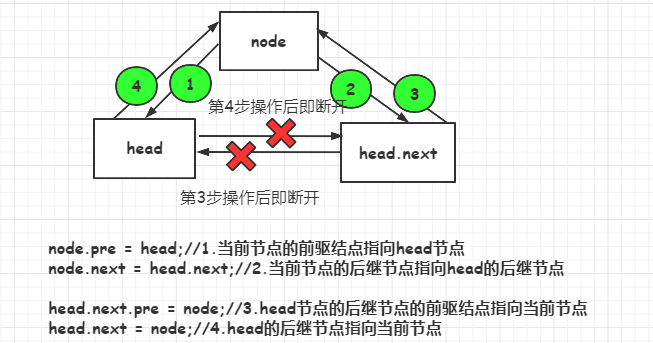
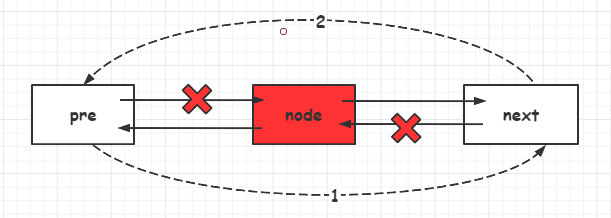
思路
方法1:模拟
Last updated