数据结构
链表
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null || l2 == null) return l1 == null ? l2 : l1;
if (l1.val > l2.val) {
l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next);
return l2;
} else {
l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);
return l1;
}
}public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null || l2 == null) {
return l1 == null ? l2 : l1;
}
ListNode head = new ListNode(0);
ListNode node = head;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
node.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
node.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
node = node.next;
}
if (l1 != null) {
node.next = l1;
} else {
node.next = l2;
}
return head.next;
}Follow Up:合并两个有序链表并去重
方法1:优先队列
方法2:堆排序
方法1:迭代

方法2:递归


方法1:迭代

方法2:递归
出口条件
逻辑
方法3:双指针

方法1:迭代

方法2:递归
方法1:双指针


方法1.一遍遍历+哈希表
方法2:两次遍历+哈希表
方法3:记忆化递归
方法4:连接-恢复


方法1:快慢指针
方法2:Hash
方法1:双指针
方法1:快慢指针+翻转


方法2:头插法

方法1:快排
方法2:归并排序
方法1:递归
方法2:迭代
方法1:头插法

方法2:迭代
树
方法1:DFS
方法2:DP

方法1:BFS
方法1:DFS
方法2:BFS
follow up
方法1:迭代
方法1:迭代
方法2:递归
方法3:Morris遍历
方法1:DFS
方法2:BFS
方法1:DFS
方法2:BFS
方法1:递归
方法2:迭代
Follow up :如何打印出路径
方法1:迭代法
方法1:DFS
最近公共祖先(LCA|Lowest Common Ancestor)

方法1:DFS



方法2:迭代

如果这棵二叉树是一棵二叉搜索树(BST)呢?
方法1:DFS
Reference
方法2:找分割点
方法1:BFS
方法2:DFS
方法1:BFS
方法2:DFS

Follow Up:1.自底向上的层序遍历如何做?
Follow Up:2.按奇偶层数锯齿层序遍历如何做?
方法1:递归+分情况讨论
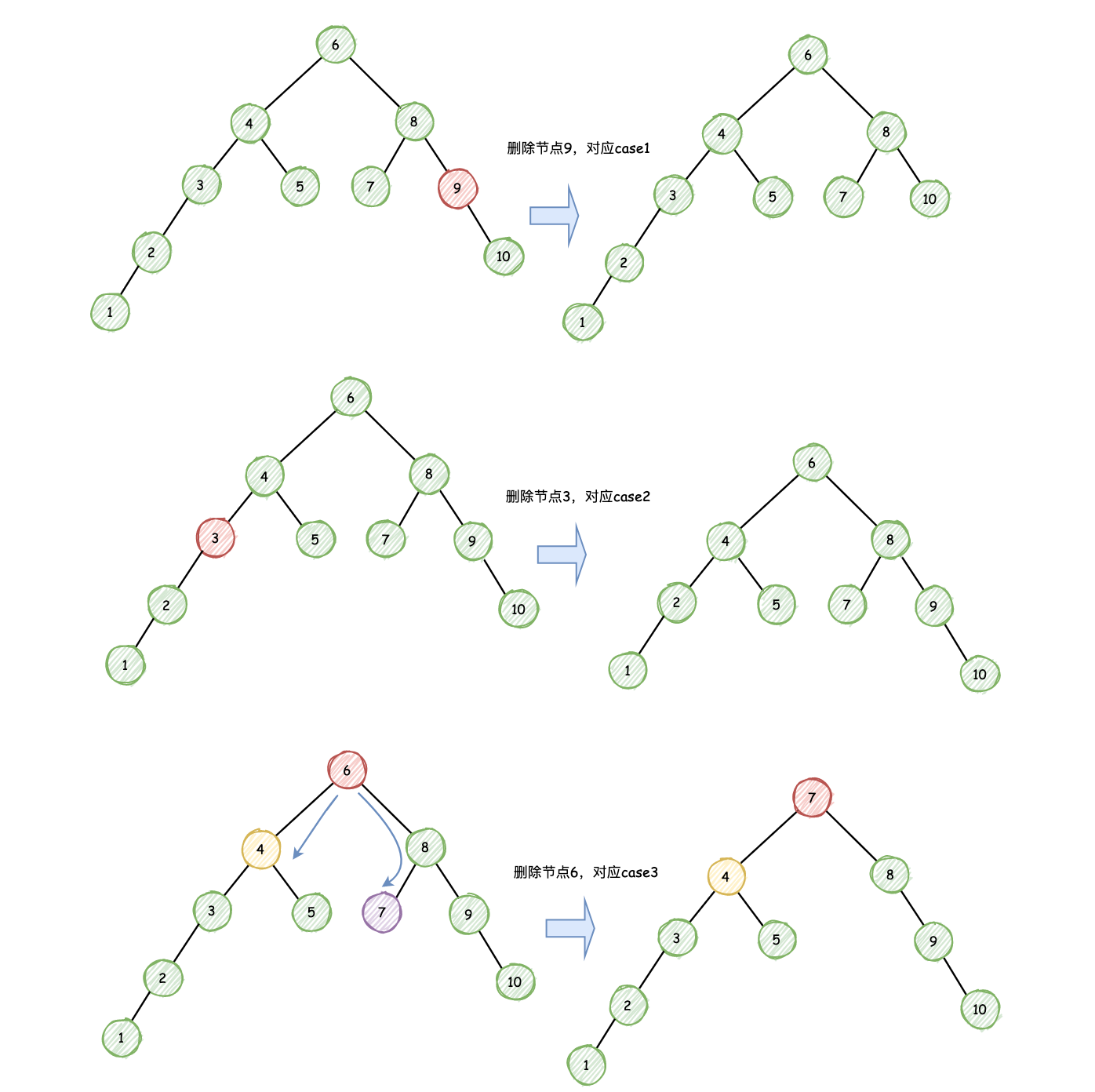
方法1:DFS
方法1:BFS
方法2:DFS
Follow Up:找树右下角的值
方法1:BFS
方法2:DFS
方法1:层序遍历
方法2:DFS
方法1:DFS
方法1:dfs
方法1:迭代-标识节点
方法2:迭代-Set
方法3:递归
方法1:递归+Set
方法2:双指针
方法1:递归
方法2:迭代
方法1:递归
方法2:递归
方法3:迭代
方法1:中序+归并
方法2:BFS
方法1:普通树+中序遍历
方法2:迭代+二分
方法3:递归
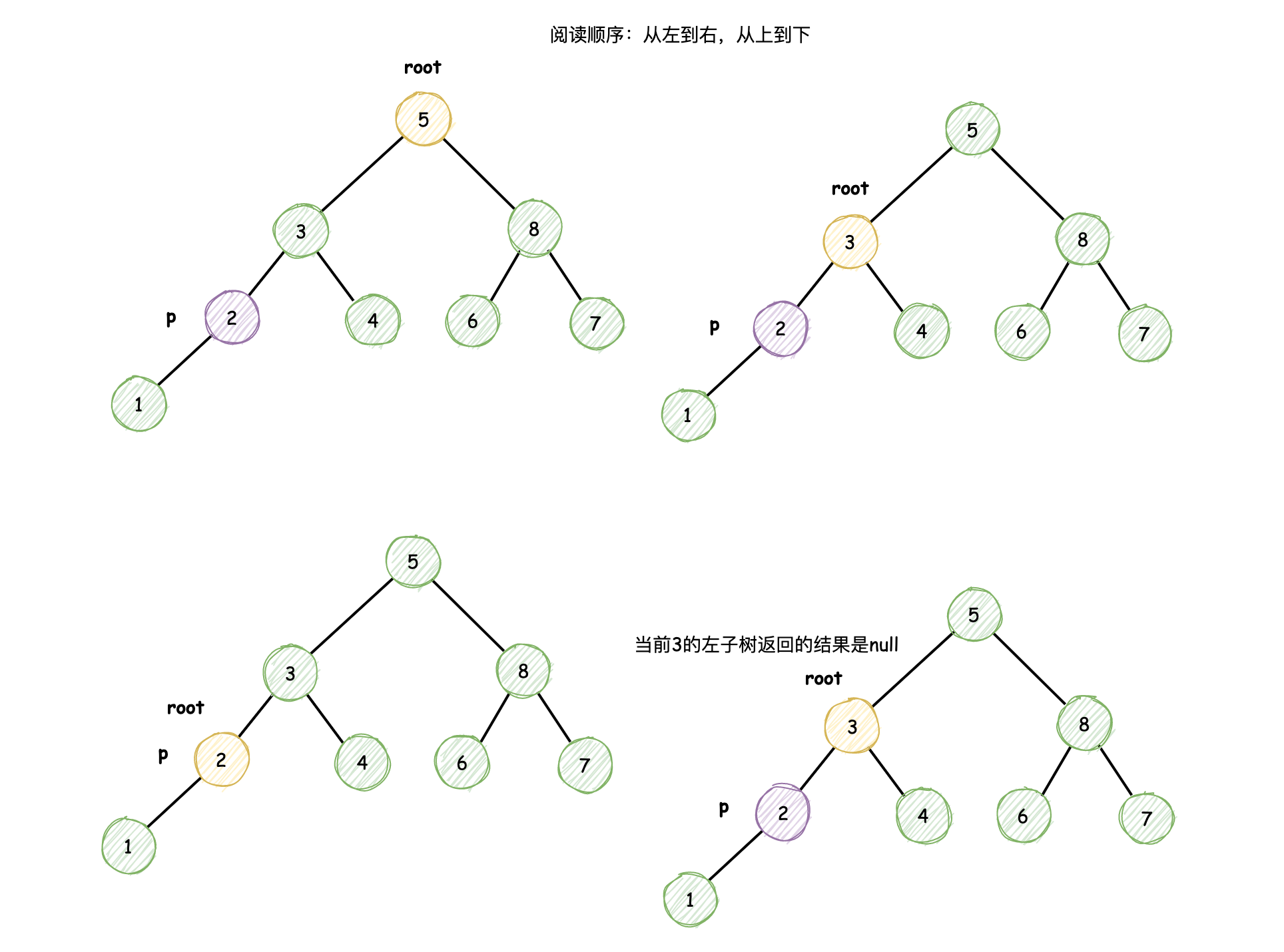
方法1:遍历
Last updated